
Hydronic Heating and Cooling
Efficient, comfortable, and healthy climate control
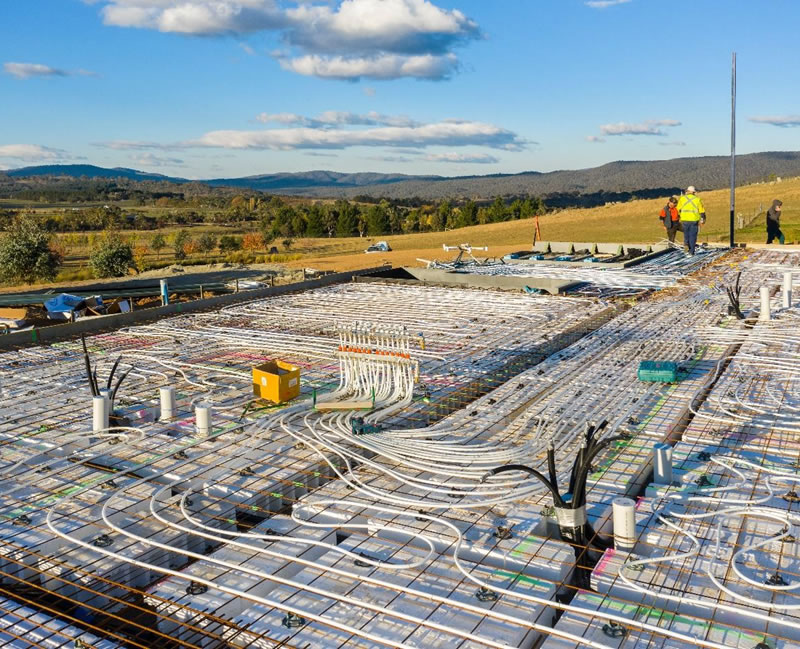

What is Hydronic Heating?
Hydronic systems use water as the medium to heat—and more recently cool—your home or building.
Water is heated or cooled from a source (boiler, heat pump) and distributed via pipes in the concrete slab, screeds, or radiators throughout the home.
The heated water running in the slab conducts through the concrete, turning the slab into a giant radiator. There is nothing like warm floors in the middle of winter. Alternatively, pipes can be distributed to radiators which radiate warmth into the rooms.
It's silent, clean, and the most comfortable and popular form of heat around the world. Forced air cannot match it.
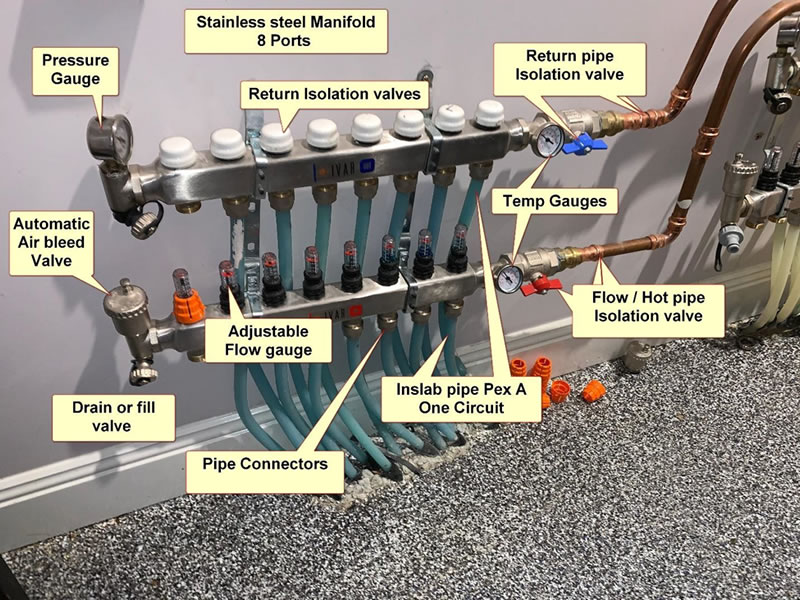
Main Components
- Manifold: The central location for all circuit pipes in the concrete slab.
-
Circuit Pipes: Pipes in the slab for each area/room (normally 16mm with oxygen barrier).
Pex A: Most common, excellent oxygen barrier.
Pert: Good alternative with oxygen barrier.
Pex B: Less common, harder to work with.
Pex Al Pex: Better for radiators, not recommended for in-slab.
- Main Flow & Return Pipes: Pex A, Pex Al Pex, or Copper (20-25mm internal diameter).
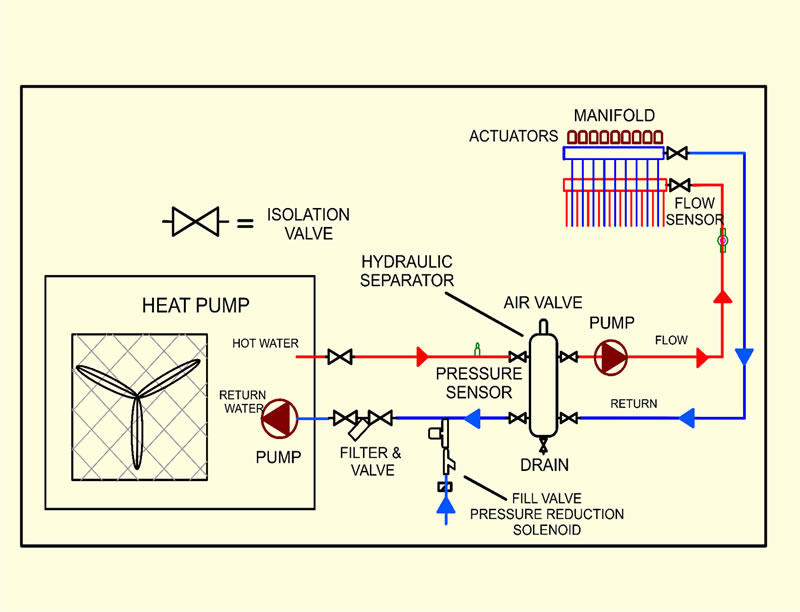
- Heat Source: Gas Boiler, Wood/Pellet Boiler, Waste Oil/Diesel Boiler, or Heat Pumps (Air-to-Water or Water-to-Water).
- Thermostat: Essential controls to manage the system. See Understanding Zoning for more detail.
Hydronic vs. Reverse Cycle Air Conditioning
Why hydronic is the superior choice for comfort and health
Reverse cycle has two main advantages: cheap installation and quick response. However, it falls short in many critical areas:
Comfort & Health
Forced air heats by convection, often feeling stuffy. It blows dust, allergens, and germs around the house—a major concern for asthma and allergy sufferers.
Installation Quality
Ducts are often poorly installed (squished or damaged), run through unconditioned roof spaces (losing heat), and are rarely cleaned.
Zoning & Efficiency
Return vents make effective zoning difficult. Moving air creates pressure differences that pull outside air into the home, reducing efficiency.
