Heat Pump Technology
The energy-efficient future of hydronic heating

Converting from Gas Boiler to Heat Pump
Why make the switch?
I generally wouldn't recommend simply removing a working condensing gas boiler unless it's ready for replacement. However, when the time comes, heat pumps are an exceptional option for hydronic heating, especially for in-slab systems.
Efficiency: Heat pumps are extremely energy efficient. 1 kWh of input produces around 4.6 kWh of heat output (COP of 4.6).
Compare this to a high-efficiency gas boiler, where 1 kWh of input produces only about 0.9 kWh of output. Coupling a heat pump with solar PV panels can reduce your running costs even further.
Types of Heat Pumps
- Air-to-Water: The standard for hydronic heating systems.
- Air-to-Air: Commonly known as reverse-cycle air conditioning.
- Ground Source (Geothermal): Highly efficient but often economically unviable in Australia due to installation costs.
Factors Affecting Output
Heat pump performance varies based on:
- Ambient air temperature
- Water inlet temperature
- Water outlet temperature
Understanding Capacity
Heat pump sizing for hydronic heating in Australia is typically rated based on these standard conditions:
Output capacity reduces with lower air temperatures or higher required water outlet temperatures.
Energy Cost Comparison
Based on typical Canberra, Australia prices
Heat Pump
$0.62
per 10kWh
- 450% Efficiency
- Electricity @ $0.28/kWh
- Solar PV compatible
Older Gas Boiler
$1.93
per 10kWh
- 70% Efficiency
- Natural Gas @ $0.135/kWh
- Fossil fuel based
Heat Pump Sizing Guide
Determine your cost savings and estimated heat pump size
1. Gas Consumption
2. Heat Pump Savings Calculation
Total Estimated Savings
Switching could save you approximately:
Annual Savings
$
Reduction
%
Recommended Heat Pump Size
Quick Sizing Guide
In-Slab Heating
Well-insulated & zoned: ~70W/m²
(e.g., 200m² home = 14kW unit)
Average insulation: ~100W/m²
(e.g., 200m² home = 20kW unit)
Radiators
Well-insulated & oversized radiators: ~100W/m²
(e.g., 200m² home = 20kW unit)
Average home: ~120-150W/m²
(e.g., 200m² home = 24-30kW unit)
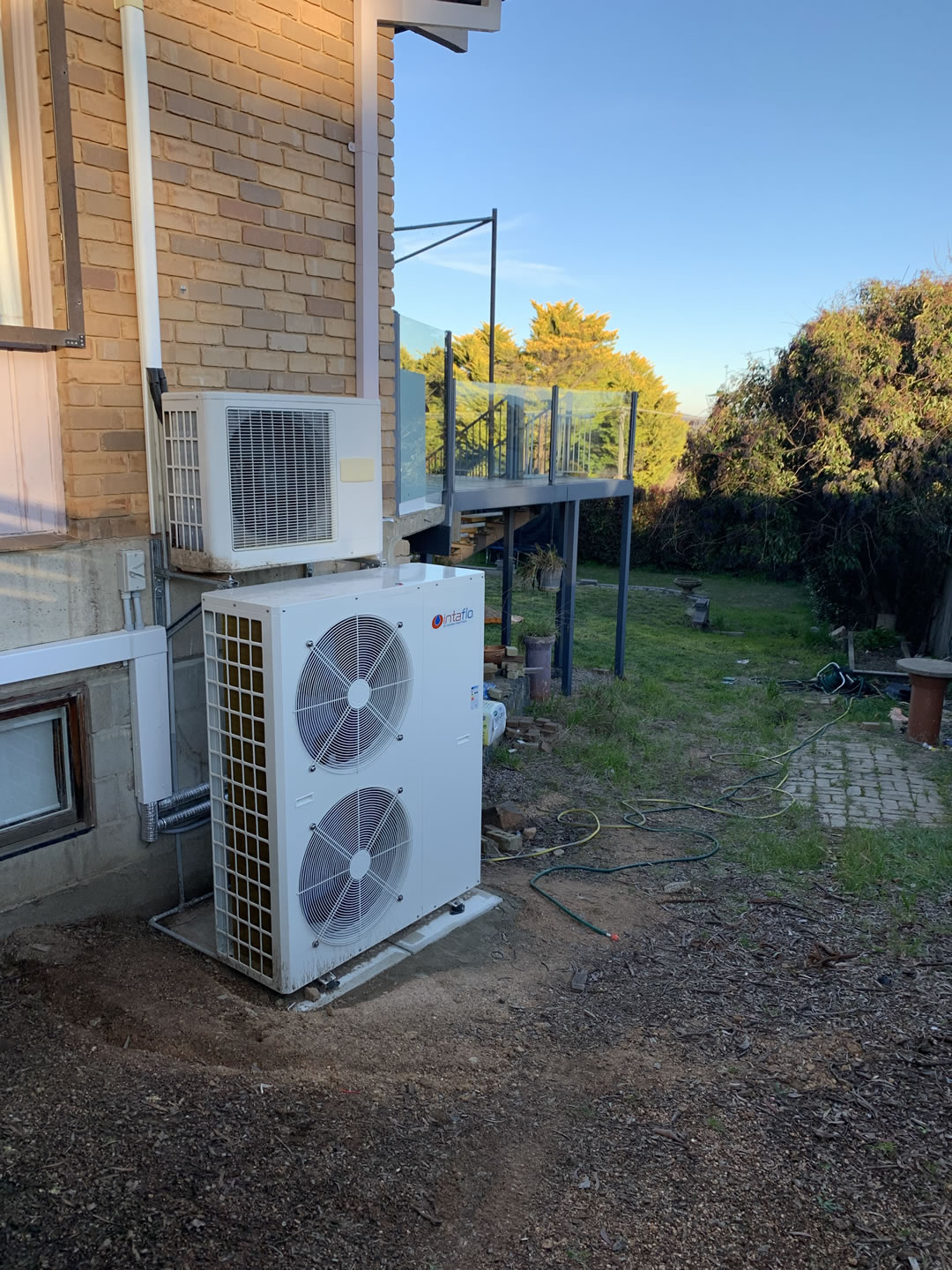
Ideal Heat Pump Positioning
Location matters for efficiency and longevity.
- Northern Aspect: Place on the north side (southern hemisphere) to gain winter sun for better performance.
- Noise Control: Install away from bedroom windows.
- Airflow: Ensure plenty of clearance around the unit, especially the front fan.
- Access: Allow space for servicing and maintenance.
- Snow Areas: Mount off the ground and consider a top cover (while maintaining airflow).
Zoning & Monitoring
Zoning improves efficiency significantly. Unlike gas boilers which have fixed capacities, heat pumps benefit greatly from tailored load management. Learn more about Zoning.

